The QBoxLayout class lines up child widgets horizontally or vertically. 更多...
继承 QLayout .
Inherited by QHBoxLayout and QVBoxLayout .
The QBoxLayout class lines up child widgets horizontally or vertically.
QBoxLayout takes the space it gets (from its parent layout or 从 parentWidget ()), divides it up into a row of boxes, and makes each managed widget fill one box.
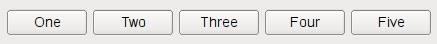
若 QBoxLayout 的取向为 Qt.Horizontal the boxes are placed in a row, with suitable sizes. Each widget (or other box) will get at least its minimum size and at most its maximum size. Any excess space is shared according to the stretch factors (more about that below).
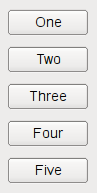
若 QBoxLayout 的取向为 Qt.Vertical , the boxes are placed in a column, again with suitable sizes.
The easiest way to create a QBoxLayout is to use one of the convenience classes, e.g. QHBoxLayout (for Qt.Horizontal boxes) or QVBoxLayout (for Qt.Vertical boxes). You can also use the QBoxLayout constructor directly, specifying its direction as LeftToRight , RightToLeft , TopToBottom ,或 BottomToTop .
If the QBoxLayout is not the top-level layout (i.e. it is not managing all of the widget's area and children), you must add it to its parent layout before you can do anything with it. The normal way to add a layout is by calling parentLayout-> addLayout ().
Once you have done this, you can add boxes to the QBoxLayout using one of four functions:
使用 insertWidget (), insertSpacing (), insertStretch () 或 insertLayout () to insert a box at a specified position in the layout.
QBoxLayout also includes two margin widths:
The margin default is provided by the style. The default margin most Qt styles specify is 9 for child widgets and 11 for windows. The spacing defaults to the same as the margin width for a top-level layout, or to the same as the parent layout.
To remove a widget from a layout, call removeWidget (). Calling QWidget.hide () on a widget also effectively removes the widget from the layout until QWidget.show () 被调用。
You will almost always want to use QVBoxLayout and QHBoxLayout rather than QBoxLayout because of their convenient constructors.
This type is used to determine the direction of a box layout.
| 常量 | 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| QBoxLayout.LeftToRight | 0 | 水平从左到右。 |
| QBoxLayout.RightToLeft | 1 | 水平从右到左。 |
| QBoxLayout.TopToBottom | 2 | 垂直从上到下。 |
| QBoxLayout.BottomToTop | 3 | 垂直从下到上。 |
parent argument, if not None, causes self to be owned by Qt instead of PyQt.
构造新 QBoxLayout with direction dir 和父级 Widget parent .
另请参阅 direction ().
QLayoutItem argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
重实现自 QLayout.addItem ().
layout argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
添加 layout to the end of the box, with serial stretch factor stretch .
另请参阅 insertLayout (), addItem (),和 addWidget ().
spacerItem argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
添加 spacerItem 到此方框布局的末尾。
该函数在 Qt 4.4 引入。
另请参阅 addSpacing () 和 addStretch ().
添加不可拉伸空间 ( QSpacerItem ) 采用尺寸 size 到 end of this box layout. QBoxLayout provides default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.
另请参阅 insertSpacing (), addItem (),和 QSpacerItem .
添加可拉伸空间 ( QSpacerItem ) with zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch 到此方框布局的末尾。
另请参阅 insertStretch (), addItem (),和 QSpacerItem .
Limits the perpendicular dimension of the box (e.g. height if the box is LeftToRight ) to a minimum of size . Other constraints may increase the limit.
另请参阅 addItem ().
添加 widget to the end of this box layout, with a stretch factor of stretch 和对齐 alignment .
The stretch factor applies only in the direction 的 QBoxLayout , and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout . Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget :sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment 。默认 alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
另请参阅 insertWidget (), addItem (), addLayout (), addStretch (), addSpacing (),和 addStrut ().
重实现自 QLayout.count ().
返回框的方向。 addWidget () 和 addSpacing () work in this direction; the stretch stretches in this direction.
另请参阅 setDirection (), QBoxLayout.Direction , addWidget (),和 addSpacing ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.expandingDirections ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.hasHeightForWidth ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.heightForWidth ().
QLayoutItem argument, if not None, causes self to be owned by Qt instead of PyQt.
插入 item 到此框布局在位置 index 。若 index is negative, the item is added at the end.
另请参阅 addItem (), insertWidget (), insertLayout (), insertStretch (),和 insertSpacing ().
layout argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
插入 layout 在位置 index , with stretch factor stretch 。若 index is negative, the layout is added at the end.
layout 变为框布局的子级。
另请参阅 addLayout () 和 insertItem ().
spacerItem argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
插入 spacerItem 在位置 index , with zero minimum size and stretch factor. If index is negative the space is added at the end.
该函数在 Qt 4.4 引入。
另请参阅 addSpacerItem (), insertStretch (),和 insertSpacing ().
插入不可拉伸空间 ( QSpacerItem ) 在位置 index ,采用 size size 。若 index is negative the space is added at the end.
The box layout has default margin and spacing. This function adds additional space.
另请参阅 addSpacing (), insertItem (),和 QSpacerItem .
插入可拉伸空间 ( QSpacerItem ) 在位置 index ,采用 zero minimum size and stretch factor stretch 。若 index 为负,空间被添加在末尾。
另请参阅 addStretch (), insertItem (),和 QSpacerItem .
插入 widget 在位置 index , with stretch factor stretch 和对齐 alignment 。若 index is negative, the widget is added at the end.
The stretch factor applies only in the direction 的 QBoxLayout , and is relative to the other boxes and widgets in this QBoxLayout . Widgets and boxes with higher stretch factors grow more.
If the stretch factor is 0 and nothing else in the QBoxLayout has a stretch factor greater than zero, the space is distributed according to the QWidget :sizePolicy() of each widget that's involved.
The alignment is specified by alignment 。默认 alignment is 0, which means that the widget fills the entire cell.
另请参阅 addWidget () 和 insertItem ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.invalidate ().
重置缓存信息。
重实现自 QLayout.itemAt ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.maximumSize ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.minimumHeightForWidth ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.minimumSize ().
将此布局的方向设为 direction .
另请参阅 direction ().
重实现自 QLayoutItem.setGeometry ().
重实现 QLayout.setSpacing (). Sets the spacing property to spacing .
另请参阅 QLayout.setSpacing () 和 spacing ().
设置拉伸因子在位置 index . to stretch .
该函数在 Qt 4.5 引入。
另请参阅 stretch ().
设置拉伸因子为 widget to stretch and returns true if widget is found in this layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
另请参阅 setAlignment ().
这是重载函数。
设置拉伸因子为布局 layout to stretch and returns true if layout 被找到在此 layout (not including child layouts); otherwise returns false.
重实现自 QLayoutItem.sizeHint ().
重实现 QLayout.spacing (). If the spacing property is valid, that value is returned. Otherwise, a value for the spacing property is computed and returned. Since layout spacing in a widget is style dependent, if the parent is a widget, it queries the style for the (horizontal or vertical) spacing of the layout. Otherwise, the parent is a layout, and it queries the parent layout for the spacing().
另请参阅 QLayout.spacing () 和 setSpacing ().
返回拉伸因子在位置 index .
该函数在 Qt 4.5 引入。
另请参阅 setStretch ().
QLayoutItem result
重实现自 QLayout.takeAt ().