The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface 对象。 更多...
继承 QObject and QPaintDevice .
Inherited by EffectWidget , SeekSlider , VideoPlayer , VideoWidget , VolumeSlider , QAbstractButton , QAbstractSlider , QAbstractSpinBox , QAxWidget , QCalendarWidget , QComboBox , QDesignerActionEditorInterface , QDesignerFormWindowInterface , QDesignerObjectInspectorInterface , QDesignerPropertyEditorInterface , QDesignerWidgetBoxInterface , QDesktopWidget , QDialog , QDialogButtonBox , QDockWidget , QFocusFrame , QFrame , QGLWidget , QGroupBox , QHelpSearchQueryWidget , QHelpSearchResultWidget , QLineEdit , QMainWindow , QMdiSubWindow , QMenu , QMenuBar , QPrintPreviewWidget , QProgressBar , QRubberBand , QSizeGrip , QSplashScreen , QSplitterHandle , QStatusBar , QSvgWidget , QTabBar , QTabWidget , QToolBar , QWebInspector , QWebView , QWizardPage and QWorkspace .
The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface 对象。
The widget is the atom of the user interface: it receives mouse, keyboard and other events from the window system, and paints a representation of itself on the screen. Every widget is rectangular, and they are sorted in a Z-order. A widget is clipped by its parent and by the widgets in front of it.
A widget that is not embedded in a parent widget is called a window. Usually, windows have a frame and a title bar, although it is also possible to create windows without such decoration using suitable 窗口标志 ). In Qt, QMainWindow and the various subclasses of QDialog are the most common window types.
Every widget's constructor accepts one or two standard arguments:
QWidget has many member functions, but some of them have little direct functionality; for example, QWidget has a font property, but never uses this itself. There are many subclasses which provide real functionality, such as QLabel , QPushButton , QListWidget ,和 QTabWidget .
A widget without a parent widget is always an independent window (top-level widget). For these widgets, setWindowTitle () 和 setWindowIcon () set the title bar and icon respectively.
Non-window widgets are child widgets, displayed within their parent widgets. Most widgets in Qt are mainly useful as child widgets. For example, it is possible to display a button as a top-level window, but most people prefer to put their buttons inside other widgets, such as QDialog .
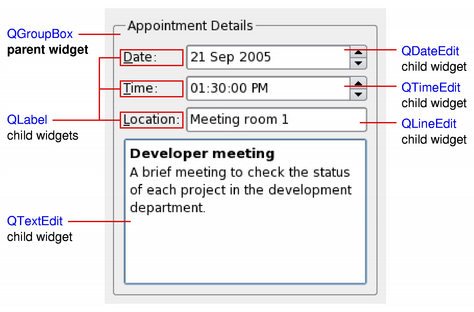
以上简图展示 QGroupBox widget being used to hold various child widgets in a layout provided by QGridLayout 。 QLabel child widgets have been outlined to indicate their full sizes.
If you want to use a QWidget to hold child widgets you will usually want to add a layout to the parent QWidget. See 布局管理 了解更多信息。
When a widget is used as a container to group a number of child widgets, it is known as a composite widget. These can be created by constructing a widget with the required visual properties - a QFrame , for example - and adding child widgets to it, usually managed by a layout. The above diagram shows such a composite widget that was created using Qt Designer .
Composite widgets can also be created by subclassing a standard widget, such as QWidget or QFrame ,和 adding the necessary layout and child widgets in the constructor of the subclass. Many of the examples provided with Qt use this approach, and it is also covered in the Qt 教程 .
由于 QWidget 是子类化的 QPaintDevice , subclasses can be used to display custom content that is composed using a series of painting operations with an instance of the QPainter class. This approach contrasts with the canvas-style approach used by the 图形视图框架 where items are added to a scene by the application and are rendered by the framework itself.
每个 Widget 履行所有描绘操作均在其 paintEvent () function. This is called whenever the widget needs to be redrawn, either as a result of some external change or when requested by the 应用程序。
指针式时钟范例 展示简单 Widget 如何处理描绘事件。
When implementing a new widget, it is almost always useful to reimplement sizeHint () 到 provide a reasonable default size for the widget and to set the correct size policy with setSizePolicy ().
By default, composite widgets which do not provide a size hint will be sized according to the space requirements of their child widgets.
The size policy lets you supply good default behavior for the layout management system, so that other widgets can contain and manage yours easily. The default size policy indicates that the size hint represents the preferred size of the widget, and this is often good enough for many widgets.
注意: The size of top-level widgets are constrained to 2/3 of the desktop's height and width. You can resize () the widget manually if these bounds are inadequate.
Widgets respond to events that are typically caused by user actions. Qt delivers events to widgets by calling specific event handler functions with instances of QEvent subclasses containing information about each event.
If your widget only contains child widgets, you probably do not need to implement any event handlers. If you want to detect a mouse click in a child widget call the child's underMouse () function inside the widget's mousePressEvent ().
Scribble example implements a wider set of events to handle mouse movement, button presses, and window resizing.
You will need to supply the behavior and content for your own widgets, but here is a brief overview of the events that are relevant to QWidget, starting with the most common ones:
Widgets that accept keyboard input need to reimplement a few more event handlers:
You may be required to also reimplement some of the less common event handlers:
There are also some rather obscure events described in the documentation for QEvent.Type . To handle these events, you need to reimplement event () directly.
The default implementation of event () handles Tab and Shift+Tab (to move the keyboard focus), and passes on most of the other events to one of the more specialized handlers above.
Events and the mechanism used to deliver them are covered in 事件系统 .
In addition to the standard widget styles for each platform, widgets can also be styled according to rules specified in a style sheet . This feature enables you to customize the appearance of specific widgets to provide visual cues to users about their purpose. For example, a button could be styled in a particular way to indicate that it performs a destructive action.
The use of widget style sheets is described in more detail in the Qt 样式表 文档。
Since Qt 4.0, QWidget automatically double-buffers its painting, so there is no need to write double-buffering code in paintEvent () to avoid flicker.
Since Qt 4.1, the Qt.WA_ContentsPropagated widget attribute has been deprecated. Instead, the contents of parent widgets are propagated by default to each of their children as long as Qt.WA_PaintOnScreen is not set. Custom widgets can be written to take advantage of this feature by updating irregular regions (to create non-rectangular child widgets), or painting with colors that have less than full alpha component. The following diagram shows how attributes and properties of a custom widget can be fine-tuned to achieve different effects.

In the above diagram, a semi-transparent rectangular child widget with an area removed is constructed and added to a parent widget (a QLabel showing a pixmap). Then, different properties and widget attributes are set to achieve different effects:
To rapidly update custom widgets with simple background colors, such as real-time plotting or graphing widgets, it is better to define a suitable background color (using setBackgroundRole () with the QPalette.Window role), set the autoFillBackground property, and only implement the necessary drawing functionality in Widget 的 paintEvent ().
To rapidly update custom widgets that constantly paint over their entire areas with opaque content, e.g., video streaming widgets, it is better to set the widget's Qt.WA_OpaquePaintEvent , avoiding any unnecessary overhead associated with repainting the widget's background.
If a widget has both the Qt.WA_OpaquePaintEvent widget attribute and the autoFillBackground property set, the Qt.WA_OpaquePaintEvent attribute takes precedence. Depending on your requirements, you should choose either one of them.
Since Qt 4.1, the contents of parent widgets are also propagated to standard Qt widgets. This can lead to some unexpected results if the parent widget is decorated in a non-standard way, as shown in the diagram below.
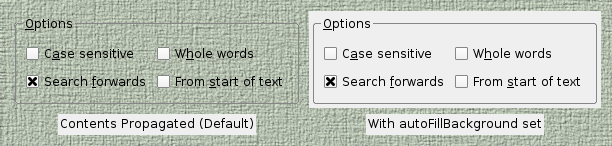
The scope for customizing the painting behavior of standard Qt widgets, without resorting to subclassing, is slightly less than that possible for custom widgets. Usually, the desired appearance of a standard widget can be achieved by setting its autoFillBackground 特性。
Since Qt 4.5, it has been possible to create windows with translucent regions on window systems that support compositing.
要在顶层 Widget 启用此特征,设置其 Qt.WA_TranslucentBackground 属性采用 setAttribute () and ensure that its background is painted with non-opaque colors in the regions you want to be partially transparent.
平台注意事项:
Introduced in Qt 4.4, alien widgets are widgets unknown to the windowing system. They do not have a native window handle associated with them. This feature significantly speeds up widget painting, resizing, and removes flicker.
Should you require the old behavior with native windows, you can choose one of the following options:
Since Qt 4.6, Softkeys are usually physical keys on a device that have a corresponding label or other visual representation on the screen that is generally located next to its physical counterpart. They are most often found on mobile phone platforms. In modern touch based user interfaces it is also possible to have softkeys that do not correspond to any physical keys. Softkeys differ from other onscreen labels in that they are contextual.
In Qt, contextual softkeys are added to a widget by calling addAction () and passing a QAction with a softkey role set on it. When the widget containing the softkey actions has focus, its softkeys should appear in the user interface. Softkeys are discovered by traversing the widget hierarchy so it is possible to define a single set of softkeys that are present at all times by calling addAction () for a given top level 小部件。
On some platforms, this concept overlaps with QMenuBar such that if no other softkeys are found and the top level widget 是 QMainWindow 包含 QMenuBar , the menubar actions may appear on one of the softkeys.
Note: Currently softkeys are only supported on the Symbian Platform.
此枚举描述如何渲染 Widget 当调用 QWidget.render ().
| 常量 | 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| QWidget.DrawWindowBackground | 0x1 | 若启用此选项,Widget 的 background is rendered into the target even if autoFillBackground is not set. By default, this option is enabled. |
| QWidget.DrawChildren | 0x2 | 若启用此选项,Widget 的 children are rendered recursively into the target. By default, this option is enabled. |
| QWidget.IgnoreMask | 0x4 | 若启用此选项,Widget 的 QWidget.mask () is ignored when rendering into the target. By default, this option is disabled. |
该枚举在 Qt 4.3 引入或被修改。
RenderFlags 类型是 typedef 对于 QFlags <RenderFlag>. It stores an OR combination of RenderFlag values.
parent argument, if not None, causes self to be owned by Qt instead of PyQt.
构造子级 Widget 为 parent ,采用 widget flags set to f .
若 parent is 0, the new widget becomes a window. If parent is another widget, this widget becomes a child window inside parent 。新的小部件被删除当其 parent 被删除。
Widget 标志自变量 f , is normally 0, but it can be set to customize the frame of a window (i.e. parent must be 0). To customize the frame, use a value composed from the bitwise OR of any of the window flags .
If you add a child widget to an already visible widget you must explicitly show the child to make it visible.
Note that the X11 version of Qt may not be able to deliver all combinations of style flags on all systems. This is because on X11, Qt can only ask the window manager, and the window manager can override the application's settings. On Windows, Qt can set whatever flags you want.
另请参阅 windowFlags .
此事件处理程序被调用采用给定 event 每当 Widget 的操作发生更改时。
另请参阅 addAction (), insertAction (), removeAction (), actions (),和 QActionEvent .
返回此 Widget 的动作列表 (可能为空)。
另请参阅 contextMenuPolicy , insertAction (),和 removeAction ().
Sets the top-level widget containing this widget to be the active window.
An active window is a visible top-level window that has the keyboard input focus.
This function performs the same operation as clicking the mouse on the title bar of a top-level window. On X11, the result depends on the Window Manager. If you want to ensure that the window is stacked on top as well you should also call raise_ (). Note that the window must be visible, otherwise activateWindow() has no effect.
On Windows, if you are calling this when the application is not currently the active one then it will not make it the active window. It will change the color of the taskbar entry to indicate that the window has changed in some way. This is because Microsoft does not allow an application to interrupt what the user is currently doing in another application.
另请参阅 isActiveWindow (), window (),和 show ().
追加动作 action to this widget's list of actions.
所有 QWidget 都有列表,针对 QAction s, however they can be represented graphically in many different ways. The default use of the QAction list (as returned by actions ()) is to create a context QMenu .
A QWidget should only have one of each action and adding an action it already has will not cause the same action to be in the widget twice.
The ownership of action 不会被转移给此 QWidget .
另请参阅 removeAction (), insertAction (), actions (),和 QMenu .
追加动作 actions to this widget's list of actions.
另请参阅 removeAction (), QMenu ,和 addAction ().
调整 Widget 大小,以拟合其内容。
此函数使用 sizeHint () if it is valid, i.e., the size hint's width and height are >= 0. Otherwise, it sets the size to the children rectangle that covers all child widgets (the union of all child widget rectangles).
For windows, the screen size is also taken into account. If the sizeHint () is less than (200, 100) and the size policy is expanding , the window will be at least (200, 100). The maximum size of a window is 2/3 of the screen's width and height.
另请参阅 sizeHint () 和 childrenRect ().
返回 Widget 的背景角色。
The background role defines the brush from the widget's palette that is used to render the background.
If no explicit background role is set, the widget inherts its parent widget's background role.
另请参阅 setBackgroundRole () 和 foregroundRole ().
This event handler can be reimplemented to handle state 改变。
The state being changed in this event can be retrieved through the event 供给。
改变事件包括: QEvent.ToolBarChange , QEvent.ActivationChange , QEvent.EnabledChange , QEvent.FontChange , QEvent.StyleChange , QEvent.PaletteChange , QEvent.WindowTitleChange , QEvent.IconTextChange , QEvent.ModifiedChange , QEvent.MouseTrackingChange , QEvent.ParentChange , QEvent.WindowStateChange , QEvent.LanguageChange , QEvent.LocaleChange , QEvent.LayoutDirectionChange .
Returns the visible child widget at the position ( x , y ) in the widget's coordinate system. If there is no visible child widget at the specified position, the function returns 0.
从 Widget 获取键盘输入聚焦。
若 Widget 有活动聚焦, 聚焦出事件 is sent to this widget to tell it that it is about to lose the focus.
This widget must enable focus setting in order to get the keyboard input focus, i.e. it must call setFocusPolicy ().
另请参阅 hasFocus (), setFocus (), focusInEvent (), focusOutEvent (), setFocusPolicy (),和 QApplication.focusWidget ().
移除任何遮罩设置通过 setMask ().
另请参阅 setMask ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature bool close() .
Closes this widget. Returns true if the widget was closed; otherwise returns false.
首先,它向 Widget 发送 QCloseEvent 。小部件 hidden 若它 accepts 关闭事件。若它 ignores the event, nothing happens. The default implementation of QWidget.closeEvent () accepts the close event.
若 Widget 拥有 Qt.WA_DeleteOnClose flag, the widget is also deleted. A close events is delivered to the widget no matter if the widget is visible or not.
QApplication.lastWindowClosed () signal is emitted when the last visible primary window (i.e. window with no parent) with the Qt.WA_QuitOnClose attribute set is closed. By default this attribute is set for all widgets except transient windows such as splash screens, tool windows, and popup menus.
此事件处理程序被调用采用给定 event when Qt receives a window close request for a top-level widget from the window system.
By default, the event is accepted and the widget is closed. You can reimplement this function to change the way the widget responds to window close requests. For example, you can prevent the window from closing by calling ignore() on all events.
Main window applications typically use reimplementations of this function to check whether the user's work has been saved and ask for permission before closing. For example, the 应用程序范例 uses a helper function to determine whether or not to close the window:
void MainWindow.closeEvent(QCloseEvent *event) { if (maybeSave()) { writeSettings(); event->accept(); } else { event->ignore(); } }
另请参阅 event (), hide (), close (), QCloseEvent ,和 应用程序范例 .
The contentsMargins function returns the widget's contents margins.
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 getContentsMargins (), setContentsMargins (), and contentsRect ().
Returns the area inside the widget's margins.
另请参阅 setContentsMargins () 和 getContentsMargins ().
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget context menu events.
处理程序被调用,当 Widget 的 contextMenuPolicy is Qt.DefaultContextMenu .
默认实现忽略上下文事件。见 QContextMenuEvent 文档编制了解更多细节。
另请参阅 event (), QContextMenuEvent ,和 customContextMenuRequested ().
Creates a new widget window if window is 0, otherwise sets the widget's window to window .
Initializes the window (sets the geometry etc.) if initializeWindow is true. If initializeWindow is false, no initialization is performed. This parameter only makes sense if window is a valid window.
Destroys the old window if destroyOldWindow is true. If destroyOldWindow is false, you are responsible for destroying the window yourself (using platform native code).
QWidget constructor calls create(0,true,true) to create a window for this widget.
释放窗口系统资源。销毁 Widget 窗口,若 destroyWindow 为 true。
destroy() calls itself recursively for all the child widgets, passing destroySubWindows 为 destroyWindow parameter. To have more control over destruction of subwidgets, destroy subwidgets selectively first.
此函数通常被调用从 QWidget 析构函数。
This event handler is called when a drag is in progress and the mouse enters this widget. The event is passed in the event 参数。
若事件被忽略,Widget 不会接收任何 拖曳移动事件 .
见 拖放文档编制 for an overview of how to provide drag-and-drop in your 应用程序。
另请参阅 QDrag and QDragEnterEvent .
This event handler is called when a drag is in progress and the mouse leaves this widget. The event is passed in the event 参数。
见 拖放文档编制 for an overview of how to provide drag-and-drop in your 应用程序。
另请参阅 QDrag and QDragLeaveEvent .
This event handler is called if a drag is in progress, and when any of the following conditions occur: the cursor enters this widget, the cursor moves within this widget, or a modifier key is pressed on the keyboard while this widget has the focus. The event is passed in the event 参数。
见 拖放文档编制 for an overview of how to provide drag-and-drop in your 应用程序。
另请参阅 QDrag and QDragMoveEvent .
This event handler is called when the drag is dropped on this widget. The event is passed in the event 参数。
见 拖放文档编制 for an overview of how to provide drag-and-drop in your 应用程序。
另请参阅 QDrag and QDropEvent .
Returns the effective window system identifier of the widget, i.e. the native parent's window system identifier.
If the widget is native, this function returns the native widget ID. Otherwise, the window ID of the first native parent widget, i.e., the top-level widget that contains this widget, is returned.
注意: We recommend that you do not store this value as it is likely to change at run-time.
该函数在 Qt 4.4 引入。
另请参阅 nativeParentWidget ().
Ensures that the widget has been polished by QStyle (i.e., has a proper font and palette).
QWidget calls this function after it has been fully constructed but before it is shown the very first time. You can call this function if you want to ensure that the widget is polished before doing an operation, e.g., the correct font size might be needed in the widget's sizeHint () reimplementation. Note that this function is called from the default implementation of sizeHint ().
Polishing is useful for final initialization that must happen after all constructors (from base classes as well as from subclasses) have been called.
If you need to change some settings when a widget is polished, reimplement event () 和处理 QEvent.Polish 事件类型。
注意: The function is declared const so that it can be called from other const functions (e.g., sizeHint ()).
另请参阅 event ().
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget enter events which are passed in the event 参数。
An event is sent to the widget when the mouse cursor enters the 小部件。
另请参阅 leaveEvent (), mouseMoveEvent (),和 event ().
重实现自 QObject.event ().
这是主事件处理程序;它处理事件 event . You can reimplement this function in a subclass, but we recommend using one of the specialized event handlers instead.
Key press and release events are treated differently from other events. event() checks for Tab and Shift+Tab and tries to move the focus appropriately. If there is no widget to move the focus to (or the key press is not Tab or Shift+Tab), event() calls keyPressEvent ().
Mouse and tablet event handling is also slightly special: only when the widget is enabled , event() will call the specialized handlers such as mousePressEvent (); otherwise it will discard the event.
This function returns true if the event was recognized, otherwise it returns false. If the recognized event was accepted (见 QEvent.accepted ), any further processing such as event propagation to the parent widget stops.
另请参阅 closeEvent (), focusInEvent (), focusOutEvent (), enterEvent (), keyPressEvent (), keyReleaseEvent (), leaveEvent (), mouseDoubleClickEvent (), mouseMoveEvent (), mousePressEvent (), mouseReleaseEvent (), moveEvent (), paintEvent (), resizeEvent (), QObject.event (),和 QObject.timerEvent ().
返回指向 Widget 的指针,采用窗口标识符/句柄 id .
The window identifier type depends on the underlying window system, see qwindowdefs.h for the actual definition. If there is no widget with this identifier, 0 is returned.
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive keyboard focus events (focus received) for the widget. The event is passed in the event 参数
Widget 通常必须 setFocusPolicy () to something other than Qt.NoFocus in order to receive focus events. (Note that the application programmer can call setFocus () on any widget, even those that do not normally accept focus.)
The default implementation updates the widget (except for windows that do not specify a focusPolicy ()).
另请参阅 focusOutEvent (), setFocusPolicy (), keyPressEvent (), keyReleaseEvent (), event (),和 QFocusEvent .
Finds a new widget to give the keyboard focus to, as appropriate for Tab , and returns true if it can find a new widget, or false if it can't.
另请参阅 focusPreviousChild ().
Finds a new widget to give the keyboard focus to, as appropriate for Tab and Shift+Tab, and returns true if it can find a new widget, or false if it can't.
若 next 为 true,此函数向前搜索,若 next 为 False,向后搜索。
Sometimes, you will want to reimplement this function. For example, a web browser might reimplement it to move its "current active link" forward or backward, and call focusNextPrevChild() only when it reaches the last or first link on the "page".
Child widgets call focusNextPrevChild() on their parent widgets, but only the window that contains the child widgets decides where to redirect focus. By reimplementing this function for an object, you thus gain control of focus traversal for all child widgets.
另请参阅 focusNextChild () 和 focusPreviousChild ().
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive keyboard focus events (focus lost) for the widget. The events is passed in the event 参数。
Widget 通常必须 setFocusPolicy () to something other than Qt.NoFocus in order to receive focus events. (Note that the application programmer can call setFocus () on any widget, even those that do not normally accept focus.)
The default implementation updates the widget (except for windows that do not specify a focusPolicy ()).
另请参阅 focusInEvent (), setFocusPolicy (), keyPressEvent (), keyReleaseEvent (), event (),和 QFocusEvent .
Finds a new widget to give the keyboard focus to, as appropriate for Shift+Tab , and returns true if it can find a new widget, or false if it can't.
另请参阅 focusNextChild ().
Returns the focus proxy, or 0 if there is no focus proxy.
另请参阅 setFocusProxy ().
Returns the last child of this widget that setFocus had been called on. For top level widgets this is the widget that will get focus in case this window gets activated
这不同于 QApplication.focusWidget (), which returns the focus widget in the currently active window.
Returns the font info for the widget's current font. Equivalent to QFontInto(widget-> font ()).
另请参阅 font (), fontMetrics (),和 setFont ().
Returns the font metrics for the widget's current font. 相当于 QFontMetrics (widget-> font ()).
另请参阅 font (), fontInfo (),和 setFont ().
返回前景角色。
前景角色定义颜色来自 Widget 的 palette that is used to draw the foreground.
If no explicit foreground role is set, the function returns a role that contrasts with the background role.
另请参阅 setForegroundRole () 和 backgroundRole ().
Returns the widget's contents margins for left , top , right ,和 bottom .
另请参阅 setContentsMargins () 和 contentsRect ().
将 Widget 订阅到给定 gesture 采有特定 flags .
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 ungrabGesture () 和 QGestureEvent .
抓取键盘输入。
此 Widget 接收所有键盘事件直到 releaseKeyboard () is called; other widgets get no keyboard events at all. Mouse events are not affected. Use grabMouse () if you want to grab that.
The focus widget is not affected, except that it doesn't receive any keyboard events. setFocus () moves the focus as usual, but the new focus widget receives keyboard events only after releaseKeyboard () 被调用。
If a different widget is currently grabbing keyboard input, that widget's grab is released first.
另请参阅 releaseKeyboard (), grabMouse (), releaseMouse (),和 focusWidget ().
抓取鼠标输入。
此 Widget 接收所有鼠标事件直到 releaseMouse () is called; other widgets get no mouse events at all. Keyboard events are not affected. Use grabKeyboard () if you want to grab that.
警告: Bugs in mouse-grabbing applications very often lock the terminal. Use this function with extreme caution, and consider using the -nograb command line option while debugging.
It is almost never necessary to grab the mouse when using Qt, as Qt grabs and releases it sensibly. In particular, Qt grabs the mouse when a mouse button is pressed and keeps it until the last button is released.
注意: 仅可见 Widget 可以抓取鼠标输入。若 isVisible () returns false 对于 Widget,小部件无法调用 grabMouse()。
注意: (Mac OS X developers) For Cocoa , calling grabMouse() on a widget only works when the mouse is inside the frame of that widget. For Carbon , it works outside the widget's frame as well, like for Windows and X11.
另请参阅 releaseMouse (), grabKeyboard (),和 releaseKeyboard ().
此函数重载 grabMouse ().
抓取鼠标输入和改变光标形状。
光标会假定形状 cursor (for as long as the mouse focus is grabbed) and this widget will be the only one to receive mouse events until releaseMouse () 被 called()。
警告: 抓取鼠标可能锁定终端。
注意: (Mac OS X developers) 见注意事项在 QWidget.grabMouse ().
另请参阅 releaseMouse (), grabKeyboard (), releaseKeyboard (),和 setCursor ().
Adds a shortcut to Qt's shortcut system that watches for the given key 序列在给定 context 。若 context is Qt.ApplicationShortcut , shortcut applies to the application as a whole. Otherwise, it is either local to this widget, Qt.WidgetShortcut , or to the window itself, Qt.WindowShortcut .
若相同 key sequence has been grabbed by several widgets, when the key 序列发生 QEvent.Shortcut event is sent to all the widgets to which it applies in a non-deterministic order, but with the ``ambiguous'' flag set to true.
警告: You should not normally need to use this function; instead create QAction s with the shortcut key sequences you require (if you also want equivalent menu options and toolbar buttons), or create QShortcut s if you just need key sequences. Both QAction and QShortcut handle all the event filtering for you, and provide signals which are triggered when the user triggers the key sequence, so are much easier to use than this low-level 函数。
另请参阅 releaseShortcut () 和 setShortcutEnabled ().
The graphicsEffect function returns a pointer to the widget's graphics effect.
If the widget has no graphics effect, 0 is returned.
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 setGraphicsEffect ().
Returns the proxy widget for the corresponding embedded widget in a graphics view; otherwise returns 0.
该函数在 Qt 4.5 引入。
另请参阅 QGraphicsProxyWidget.createProxyForChildWidget () and QGraphicsScene.addWidget ().
返回此 Widget 的首选高度,给定宽度 w .
If this widget has a layout, the default implementation returns the layout's preferred height. if there is no layout, the default implementation returns -1 indicating that the preferred height does not depend on the width.
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void hide() .
隐藏 Widget。此函数相当于 setVisible(false).
注意: If you are working with QDialog or its subclasses and you invoke the show () function after this function, the dialog will be displayed in its original position.
另请参阅 hideEvent (), isHidden (), show (), setVisible (), isVisible (),和 close ().
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget hide events. The event is passed in the event 参数。
Hide events are sent to widgets immediately after they have been hidden.
Note: A widget receives spontaneous show and hide events when its mapping status is changed by the window system, e.g. a spontaneous hide event when the user minimizes the window, and a spontaneous show event when the window is restored again. After receiving a spontaneous hide event, a widget is still considered visible in the sense of isVisible ().
另请参阅 visible , event (),和 QHideEvent .
This function returns the QInputContext for this widget. By default the input context is inherited from the widgets parent. For toplevels it is inherited from QApplication .
You can override this and set a special input context for this widget by using the setInputContext () 方法。
另请参阅 setInputContext ().
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive Input Method composition events. This handler is called when the state of the input method changes.
注意:当创建自定义文本编辑 Widget 时, Qt.WA_InputMethodEnabled 窗口属性必须被明确设置 (使用 setAttribute () function) in order to receive input method events.
The default implementation calls event->ignore(), which rejects the Input Method event. See the QInputMethodEvent documentation for more details.
另请参阅 event () 和 QInputMethodEvent .
This method is only relevant for input widgets. It is used by the input method to query a set of properties of the widget to be able to support complex input method operations as support for surrounding text and reconversions.
query 指定要查询的特性。
另请参阅 inputMethodEvent (), QInputMethodEvent , QInputContext ,和 inputMethodHints .
插入动作 action to this widget's list of actions, before the action before 。它追加动作,若 before is 0 or before is not a valid action for this 小部件。
A QWidget should only have one of each action.
另请参阅 removeAction (), addAction (), QMenu , contextMenuPolicy ,和 actions ().
插入动作 actions to this widget's list of actions, before the action before 。它追加动作,若 before is 0 or before is not a valid action for this 小部件。
A QWidget can have at most one of each action.
另请参阅 removeAction (), QMenu , insertAction (),和 contextMenuPolicy .
Returns true if this widget is a parent, (or grandparent and so on to any level), of the given child , and both widgets are within the same window; otherwise returns false.
Returns true if this widget would become enabled if ancestor is enabled; otherwise returns false.
This is the case if neither the widget itself nor every parent up to but excluding ancestor has been explicitly disabled.
isEnabledTo(0) is equivalent to isEnabled ().
另请参阅 setEnabled () 和 enabled .
Returns true if the widget is hidden, otherwise returns false.
隐藏 Widget 才变为可见当 show () is called on it. It will not be automatically shown when the parent is shown.
要校验可见性,使用 ! isVisible () instead (notice the exclamation mark).
isHidden() 隐含 ! isVisible (), but a widget can be not visible and not hidden at the same time. This is the case for widgets that are children of widgets that are not visible.
Widget 被隐藏,若:
Returns true if this widget would become visible if ancestor is shown; otherwise returns false.
The true case occurs if neither the widget itself nor any parent up to but excluding ancestor 已被明确隐藏。
This function will still return true if the widget is obscured by other windows on the screen, but could be physically visible if it or they were to be moved.
isVisibleTo(0) 等同于 isVisible ().
另请参阅 show (), hide (),和 isVisible ().
Returns true if the widget is an independent window, otherwise returns false.
A window is a widget that isn't visually the child of any other widget and that usually has a frame and a 窗口标题 .
窗口可以拥有 parent widget . It will then be grouped with its parent and deleted when the parent is deleted, minimized when the parent is minimized etc. If supported by the window manager, it will also have a common taskbar entry with its parent.
QDialog and QMainWindow widgets are by default windows, even if a parent widget is specified in the constructor. This behavior is specified by the Qt.Window 标志。
另请参阅 window (), isModal (),和 parentWidget ().
Returns the widget that is currently grabbing the keyboard input.
If no widget in this application is currently grabbing the keyboard, 0 is returned.
另请参阅 grabMouse () and mouseGrabber ().
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive key press events for the widget.
widget 必须调用 setFocusPolicy () to accept focus initially and have focus in order to receive a key press 事件。
若重实现此处理程序,非常重要的是 call the base class implementation if you do not act upon the key.
The default implementation closes popup widgets if the user presses Esc. Otherwise the event is ignored, so that the widget's parent can interpret it.
注意: QKeyEvent starts with isAccepted() == true, so you do not need to call QKeyEvent.accept () - just do not call the base class implementation if you act upon the key.
另请参阅 keyReleaseEvent (), setFocusPolicy (), focusInEvent (), focusOutEvent (), event (), QKeyEvent ,和 俄罗斯方块范例 .
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive key release events for the widget.
Widget 必须 accept focus 初始和 have focus 为接收键释放事件。
若重实现此处理程序,非常重要的是 call the base class implementation if you do not act upon the key.
The default implementation ignores the event, so that the widget's parent can interpret it.
注意: QKeyEvent starts with isAccepted() == true, so you do not need to call QKeyEvent.accept () - just do not call the base class implementation if you act upon the key.
另请参阅 keyPressEvent (), QKeyEvent.ignore (), setFocusPolicy (), focusInEvent (), focusOutEvent (), event (),和 QKeyEvent .
返回安装在此 Widget 上的布局管理器,或 0 if no layout manager is installed.
The layout manager sets the geometry of the widget's children that have been added to the layout.
另请参阅 setLayout (), sizePolicy (),和 布局管理 .
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget leave events which are passed in the event 参数。
A leave event is sent to the widget when the mouse cursor leaves the widget.
另请参阅 enterEvent (), mouseMoveEvent (),和 event ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void lower() .
Lowers the widget to the bottom of the parent widget's stack.
After this call the widget will be visually behind (and therefore obscured by) any overlapping sibling widgets.
另请参阅 raise_ () 和 stackUnder ().
翻译 Widget 坐标 pos from the coordinate system of parent 到此 Widget 的坐标系统。 parent must not be 0 and must be a parent of the calling 小部件。
另请参阅 mapTo (), mapFromParent (), mapFromGlobal (),和 underMouse ().
翻译全局屏幕坐标 pos to widget coordinates.
另请参阅 mapToGlobal (), mapFrom (),和 mapFromParent ().
翻译父级 Widget 坐标 pos to widget coordinates.
如同 mapFromGlobal () if the widget has no parent.
另请参阅 mapToParent (), mapFrom (), mapFromGlobal (),和 underMouse ().
翻译 Widget 坐标 pos to the coordinate system of parent 。 parent must not be 0 and must be a parent of the calling widget.
另请参阅 mapFrom (), mapToParent (), mapToGlobal (),和 underMouse ().
翻译 Widget 坐标 pos to global screen coordinates. For example, mapToGlobal(QPoint(0,0)) would give the global coordinates of the top-left pixel of the 小部件。
另请参阅 mapFromGlobal (), mapTo (),和 mapToParent ().
翻译 Widget 坐标 pos to a coordinate in the parent widget.
如同 mapToGlobal () if the widget has no parent.
另请参阅 mapFromParent (), mapTo (), mapToGlobal (),和 underMouse ().
Returns the mask currently set on a widget. If no mask is set the return value will be an empty region.
另请参阅 setMask (), clearMask (), QRegion.isEmpty (),和 异形时钟范例 .
重实现自 QPaintDevice.metric ().
内部实现的虚拟 QPaintDevice.metric () 函数。
m 是要获得的指标。
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive mouse double click events for the 小部件。
The default implementation generates a normal mouse press 事件。
注意: The widget will also receive mouse press and mouse release events in addition to the double click event. It is up to the developer to ensure that the application interprets these events correctly.
另请参阅 mousePressEvent (), mouseReleaseEvent (), mouseMoveEvent (), event (),和 QMouseEvent .
Returns the widget that is currently grabbing the mouse input.
If no widget in this application is currently grabbing the mouse, 0 is returned.
另请参阅 grabMouse () and keyboardGrabber ().
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive mouse move events for the widget.
If mouse tracking is switched off, mouse move events only occur if a mouse button is pressed while the mouse is being moved. If mouse tracking is switched on, mouse move events occur even if no mouse button is pressed.
QMouseEvent.pos () reports the position of the mouse cursor, relative to this widget. For press and release events, the position is usually the same as the position of the last mouse move event, but it might be different if the user's hand shakes. This is a feature of the underlying window system, not Qt.
If you want to show a tooltip immediately, while the mouse is moving (e.g., to get the mouse coordinates with QMouseEvent.pos () and show them as a tooltip), you must first enable mouse tracking as described above. Then, to ensure that the tooltip is updated immediately, you must call QToolTip.showText () 而不是 setToolTip () 在 your implementation of mouseMoveEvent().
另请参阅 setMouseTracking (), mousePressEvent (), mouseReleaseEvent (), mouseDoubleClickEvent (), event (), QMouseEvent ,和 涂鸦范例 .
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive mouse press events for the widget.
If you create new widgets in the mousePressEvent() the mouseReleaseEvent () may not end up where you expect, depending on the underlying window system (or X11 window manager), the widgets' location and maybe more.
The default implementation implements the closing of popup widgets when you click outside the window. For other widget types it does nothing.
另请参阅 mouseReleaseEvent (), mouseDoubleClickEvent (), mouseMoveEvent (), event (), QMouseEvent ,和 涂鸦范例 .
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive mouse release events for the widget.
另请参阅 mousePressEvent (), mouseDoubleClickEvent (), mouseMoveEvent (), event (), QMouseEvent ,和 涂鸦范例 .
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget move events which are passed in the event 参数。 When the widget receives this event, it is already at the new position.
可访问旧位置透过 QMoveEvent.oldPos ().
另请参阅 resizeEvent (), event (), move (),和 QMoveEvent .
Returns the native parent for this widget, i.e. the next ancestor widget that has a system identifier, or 0 if it does not have any native parent.
该函数在 Qt 4.4 引入。
另请参阅 effectiveWinId ().
返回在此 Widget 聚焦链中的下一小部件。
另请参阅 previousInFocusChain ().
将 Widget 窗口标志设为 flags , without 告诉窗口系统。
警告: Do not call this function unless you really know what you're doing.
另请参阅 setWindowFlags ().
重实现自 QPaintDevice.paintEngine ().
返回 Widget 的描绘引擎。
Note that this function should not be called explicitly by the user, since it's meant for reimplementation purposes only. The function is called by Qt internally, and the default implementation may not always return a valid pointer.
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive paint events passed in event .
A paint event is a request to repaint all or part of a widget. It can happen for one of the following reasons:
Many widgets can simply repaint their entire surface when asked to, but some slow widgets need to optimize by painting only the requested region: QPaintEvent.region (). This speed optimization does not change the result, as painting is clipped to that region during event processing. QListView and QTableView 会这样做,例如。
Qt also tries to speed up painting by merging multiple paint events into one. When update () 是 called several times or the window system sends several paint events, Qt merges these events into one event with a larger region (见 QRegion.united ())。 repaint () function does not permit this optimization, so we suggest using update () 每当可能时。
When the paint event occurs, the update region has normally been erased, so you are painting on the widget's background.
背景可以被设置使用 setBackgroundRole () 和 setPalette ().
从 Qt 4.0 起, QWidget automatically double-buffers its painting, so there is no need to write double-buffering code in paintEvent() to avoid flicker.
Note for the X11 platform : It is possible to toggle global double buffering by calling qt_x11_set_global_double_buffer() 。例如,
... extern void qt_x11_set_global_double_buffer(bool); qt_x11_set_global_double_buffer(false); ...
注意: 通常,应该克制调用 update () 或 repaint () inside a paintEvent(). 例如:调用 update () 或 repaint () on children inside a paintevent() results in undefined behavior; the child may or may not get a paint event.
警告: If you are using a custom paint engine without Qt's backingstore, Qt.WA_PaintOnScreen 必须是 set. Otherwise, QWidget.paintEngine () will never be called; the backingstore will be used instead.
另请参阅 event (), repaint (), update (), QPainter , QPixmap , QPaintEvent ,和 指针式时钟范例 .
Returns the parent of this widget, or 0 if it does not have any parent widget.
The previousInFocusChain function returns the previous widget in this widget's focus chain.
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 nextInFocusChain ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void raise() .
把此 Widget 提升到父级 Widget 的堆栈顶部。
After this call the widget will be visually in front of any overlapping sibling widgets.
注意: 当使用 activateWindow (), you can call this function to ensure that the window is stacked on top.
另请参阅 lower () 和 stackUnder ().
释放键盘抓取。
另请参阅 grabKeyboard (), grabMouse (),和 releaseMouse ().
释放鼠标抓取。
另请参阅 grabMouse (), grabKeyboard (),和 releaseKeyboard ().
删除快捷方式采用给定 id from Qt's shortcut system. The widget will no longer receive QEvent.Shortcut events for the shortcut's key sequence (unless it has other shortcuts with the same key sequence).
警告: You should not normally need to use this function since Qt's shortcut system removes shortcuts automatically when their parent widget is destroyed. It is best to use QAction or QShortcut to handle shortcuts, since they are easier to use than this low-level function. Note also that this is an expensive operation.
另请参阅 grabShortcut () 和 setShortcutEnabled ().
移除动作 action from this widget's list of actions.
另请参阅 insertAction (), actions (),和 insertAction ().
渲染 sourceRegion 的此 Widget 到 target 使用 renderFlags to determine how to render. Rendering starts at targetOffset 在 target . For example:
QPixmap pixmap(widget->size()); widget->render(&pixmap);
若 sourceRegion 是 null 区域,此函数将使用 QWidget.rect () as the region, i.e. the entire widget.
确保调用 QPainter.end () 为 target 设备的活动描绘器 (若有的话) 在渲染之前。例如:
QPainter painter(this); ... painter.end(); myWidget->render(this);
注意: To obtain the contents of an OpenGL widget, use QGLWidget.grabFrameBuffer () or QGLWidget.renderPixmap () 代替。
该函数在 Qt 4.3 引入。
这是重载函数。
将 Widget 渲染到 painter 's QPainter.device ().
变换和设置应用于 painter will be used when rendering.
注意: painter must be active. On Mac OS X the widget will be rendered into a QPixmap 然后绘制通过 painter .
另请参阅 QPainter.device ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void repaint() .
直接重新绘制 Widget 通过调用 paintEvent () immediately, unless updates are disabled or the widget is hidden.
We suggest only using repaint() if you need an immediate repaint, for example during animation. In almost all circumstances update () is better, as it permits Qt to optimize for speed and minimize flicker.
警告: If you call repaint() in a function which may itself be called from paintEvent (), you may get infinite recursion. The update () function never causes recursion.
另请参阅 update (), paintEvent (),和 setUpdatesEnabled ().
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget resize events which are passed in the event parameter. When resizeEvent() is called, the widget already has its new geometry. The old size is accessible through QResizeEvent.oldSize ().
The widget will be erased and receive a paint event immediately after processing the resize event. No drawing need be (or should be) done inside this handler.
另请参阅 moveEvent (), event (), resize (), QResizeEvent , paintEvent (),和 涂鸦范例 .
Restores the geometry and state top-level widgets stored in the byte array geometry . Returns true on success; otherwise returns false.
If the restored geometry is off-screen, it will be modified to be inside the available screen geometry.
要还原保存几何体使用 QSettings ,可以使用的代码像这样:
QSettings settings("MyCompany", "MyApp"); myWidget->restoreGeometry(settings.value("myWidget/geometry").toByteArray());
见 窗口几何体 文档编制,了解有关窗口几何体问题的概述。
使用 QMainWindow.restoreState () 到 restore the geometry and the state of toolbars and dock widgets.
该函数在 Qt 4.2 引入。
另请参阅 saveGeometry (), QSettings , QMainWindow.saveState (),和 QMainWindow.restoreState ().
保存顶层 Widget 的当前几何体及状态。
To save the geometry when the window closes, you can implement a close event like this:
void MyWidget.closeEvent(QCloseEvent *event) { QSettings settings("MyCompany", "MyApp"); settings.setValue("geometry", saveGeometry()); QWidget.closeEvent(event); }
见 窗口几何体 文档编制,了解有关窗口几何体问题的概述。
使用 QMainWindow.saveState () to save the geometry and the state of toolbars and dock widgets.
该函数在 Qt 4.2 引入。
另请参阅 restoreGeometry (), QMainWindow.saveState (),和 QMainWindow.restoreState ().
卷动 Widget 包括其子级 dx pixels to the right and dy 向下。两者 dx and dy may be negative.
After scrolling, the widgets will receive paint events for the areas that need to be repainted. For widgets that Qt knows to be opaque, this is only the newly exposed parts. For example, if an opaque widget is scrolled 8 pixels to the left, only an 8-pixel wide stripe at the right edge needs updating.
Since widgets propagate the contents of their parents by default, you need to set the autoFillBackground 特性,或使用 setAttribute () 去设置 Qt.WA_OpaquePaintEvent 属性,以使 Widget 变得不透明。
For widgets that use contents propagation, a scroll will cause an update of the entire scroll area.
另请参阅 Transparency and Double Buffering .
这是重载函数。
此版本仅卷动 r and does not move the children of the widget.
若 r 为空或无效,结果不确定。
另请参阅 QScrollArea .
设置属性 attribute 在此 Widget 若 on 为 true;否则清零属性。
另请参阅 testAttribute ().
将 Widget 背景角色设为 role .
The background role defines the brush from the widget's palette that is used to render the background.
若 role is QPalette.NoRole , then the widget inherits its parent's background role.
Note that styles are free to choose any color from the palette. You can modify the palette or set a style sheet if you don't achieve the result you want with setBackgroundRole().
另请参阅 backgroundRole () 和 foregroundRole ().
Sets the margins around the contents of the widget to have the sizes left , top , right ,和 bottom 。 margins are used by the layout system, and may be used by subclasses to specify the area to draw in (e.g. excluding the frame).
更改边距将触发 resizeEvent ().
另请参阅 contentsMargins (), contentsRect (),和 getContentsMargins ().
这是重载函数。
The setContentsMargins function sets the margins around the widget's contents.
Sets the margins around the contents of the widget to have the sizes determined by margins . The margins are used by the layout system, and may be used by subclasses to specify the area to draw in (e.g. excluding the frame).
更改边距将触发 resizeEvent ().
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 contentsRect () 和 getContentsMargins ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setDisabled(bool) .
禁用 Widget 输入事件若 disable is true; otherwise enables input events.
见 enabled 文档编制,了解更多信息。
另请参阅 isEnabledTo (), QKeyEvent , QMouseEvent ,和 changeEvent ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setEnabled(bool) .
Sets both the minimum and maximum heights of the widget to h without changing the widths. Provided for convenience.
另请参阅 sizeHint (), minimumSize (), maximumSize (),和 setFixedSize ().
Sets both the minimum and maximum sizes of the widget to s , thereby preventing it from ever growing or shrinking.
这将覆盖默认尺寸约束设置通过 QLayout .
要移除约束,将尺寸设为 QWIDGETSIZE_MAX .
Alternatively, if you want the widget to have a fixed size based on its contents, you can call QLayout.setSizeConstraint( QLayout.SetFixedSize );
另请参阅 maximumSize and minimumSize .
这是重载函数。
把 Widget 的宽度设置为 w 且高度为 h .
把 Widget 的最小 最大宽度设为 w without changing the heights. Provided for convenience.
另请参阅 sizeHint (), minimumSize (), maximumSize (),和 setFixedSize ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setFocus() .
Gives the keyboard input focus to this widget (or its focus proxy) if this widget or one of its parents is the 活动窗口 。 reason argument will be passed into any focus event sent from this function, it is used to give an explanation of what caused the widget to get focus. If the window is not active, the widget will be given the focus when the window becomes active.
First, a focus out event is sent to the focus widget (if any) to tell it that it is about to lose the focus. Then a focus in event is sent to this widget to tell it that it just received the focus. (Nothing happens if the focus in and focus out widgets are the same.)
注意: On embedded platforms, setFocus() will not cause an input panel to be opened by the input method. If you want this to happen, you have to send a QEvent.RequestSoftwareInputPanel event to the widget yourself.
setFocus() gives focus to a widget regardless of its focus policy, but does not clear any keyboard grab (see grabKeyboard ()).
Be aware that if the widget is hidden, it will not accept focus until it is shown.
警告: If you call setFocus() in a function which may itself be called from focusOutEvent () 或 focusInEvent (), you may get an infinite recursion.
另请参阅 hasFocus (), clearFocus (), focusInEvent (), focusOutEvent (), setFocusPolicy (), focusWidget (), QApplication.focusWidget (), grabKeyboard (), grabMouse (), Keyboard Focus ,和 QEvent.RequestSoftwareInputPanel .
这是重载函数。
Gives the keyboard input focus to this widget (or its focus proxy) if this widget or one of its parents is the 活动窗口 .
把 Widget 的聚焦代理设为小部件 w 。若 w is 0, the function resets this widget to have no focus proxy.
Some widgets can "have focus", but create a child widget, such as QLineEdit , to actually handle the focus. In this case, the widget can set the line edit to be its focus proxy.
setFocusProxy() sets the widget which will actually get focus when "this widget" gets it. If there is a focus proxy, setFocus () 和 hasFocus () operate on the focus proxy.
另请参阅 focusProxy ().
把 Widget 的前景角色设为 role .
前景角色定义颜色来自 Widget 的 palette that is used to draw the foreground.
若 role is QPalette.NoRole , the widget uses a foreground role that contrasts with the background role.
Note that styles are free to choose any color from the palette. You can modify the palette or set a style sheet if you don't achieve the result you want with setForegroundRole().
另请参阅 foregroundRole () 和 backgroundRole ().
effect argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
The setGraphicsEffect function is for setting the widget's graphics effect.
集 effect as the widget's effect. If there already is an effect installed on this widget, QWidget will delete the existing effect before installing the new effect .
若 effect is the installed on a different widget, setGraphicsEffect() will remove the effect from the widget and install it on this widget.
QWidget takes ownership of effect .
注意: This function will apply the effect on itself and all its children.
注意: Graphics effects are not supported on Mac, so they will not cause any difference to the rendering of the widget.
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 graphicsEffect ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setHidden(bool) .
便利函数,相当于 setVisible(! hidden ).
另请参阅 isHidden ().
QInputContext argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
This function sets the input context context on this 小部件。
Qt takes ownership of the given input context .
另请参阅 inputContext ().
QLayout argument has it's ownership transferred to Qt.
将此 Widget 的布局管理器设为 layout .
如果此 Widget 已安装了布局管理器, QWidget won't let you install another. You must first delete the existing layout manager (returned by layout ()) before you can call setLayout() with the new layout.
若 layout is the layout manger on a different widget, setLayout() will reparent the layout and make it the layout manager for this widget.
范例:
QVBoxLayout *layout = new QVBoxLayout;
layout->addWidget(formWidget);
setLayout(layout);
An alternative to calling this function is to pass this widget to the layout's constructor.
QWidget will take ownership of layout .
促使 Widget 像素仅与 bitmap has a corresponding 1 bit to be visible. If the region includes pixels outside the rect () of the widget, window system controls in that area may or may not be visible, depending on the platform.
Note that this effect can be slow if the region is particularly complex.
The following code shows how an image with an alpha channel can be used to generate a mask for a widget:
QLabel topLevelLabel;
QPixmap pixmap(":/images/tux.png");
topLevelLabel.setPixmap(pixmap);
topLevelLabel.setMask(pixmap.mask());
The label shown by this code is masked using the image it contains, giving the appearance that an irregularly-shaped image is being drawn directly onto the screen.
Masked widgets receive mouse events only on their visible portions.
另请参阅 mask (), clearMask (), windowOpacity (),和 异形时钟范例 .
这是重载函数。
促使 Widget 部分仅重叠 region 才可见。若区域包括像素超出 rect () of the widget, window system controls in that area may or may not be visible, depending on the platform.
Note that this effect can be slow if the region is particularly complex.
另请参阅 windowOpacity .
parent argument, if not None, causes self to be owned by Qt instead of PyQt.
将 Widget 父级设为 parent , and resets the window flags. The widget is moved to position (0, 0) in its new parent.
If the new parent widget is in a different window, the reparented widget and its children are appended to the end of the tab chain of the new parent widget, in the same internal order as before. If one of the moved widgets had keyboard focus, setParent() calls clearFocus () for that widget.
If the new parent widget is in the same window as the old parent, setting the parent doesn't change the tab order or keyboard focus.
If the "new" parent widget is the old parent widget, this function does nothing.
注意: The widget becomes invisible as part of changing its parent, even if it was previously visible. You must call show () to make the widget visible 再次。
警告: It is very unlikely that you will ever need this function. If you have a widget that changes its content dynamically, it is far easier to use QStackedWidget .
另请参阅 setWindowFlags ().
parent argument, if not None, causes self to be owned by Qt instead of PyQt.
这是重载函数。
此函数还接受 Widget 标志, f as an 自变量。
若 enable is true, auto repeat of the shortcut with the given id is enabled; otherwise it is disabled.
该函数在 Qt 4.2 引入。
另请参阅 grabShortcut () 和 releaseShortcut ().
若 enable is true, the shortcut with the given id is enabled; otherwise the shortcut is disabled.
警告: You should not normally need to use this function since Qt's shortcut system enables/disables shortcuts automatically as widgets become hidden/visible and gain or lose focus. It is best to use QAction or QShortcut to handle shortcuts, since they are easier to use than this low-level function.
另请参阅 grabShortcut () 和 releaseShortcut ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setShown(bool) .
Sets the widget's GUI style to style . The ownership of the style object is not transferred.
If no style is set, the widget uses the application's style, QApplication.style () 代替。
Setting a widget's style has no effect on existing or future child widgets.
警告: This function is particularly useful for demonstration purposes, where you want to show Qt's styling capabilities. Real applications should avoid it and use one consistent GUI style instead.
警告: Qt style sheets are currently not supported for custom QStyle subclasses. We plan to address this in some future release.
另请参阅 style (), QStyle , QApplication.style (),和 QApplication.setStyle ().
Puts the second widget after the first widget in the focus order.
Note that since the tab order of the second widget is changed, you should order a chain like this:
setTabOrder(a, b); // a to b setTabOrder(b, c); // a to b to c setTabOrder(c, d); // a to b to c to d
not 像这样:
// WRONG setTabOrder(c, d); // c to d setTabOrder(a, b); // a to b AND c to d setTabOrder(b, c); // a to b to c, but not c to d
若 first or second has a focus proxy, setTabOrder() correctly substitutes the proxy.
另请参阅 setFocusPolicy (), setFocusProxy (),和 Keyboard Focus .
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setVisible(bool) .
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void setWindowModified(bool) .
把窗口角色设为 role . This only makes sense for windows on X11.
另请参阅 windowRole ().
把窗口状态设为 windowState . The window state is a OR'ed combination of Qt.WindowState : Qt.WindowMinimized , Qt.WindowMaximized , Qt.WindowFullScreen ,和 Qt.WindowActive .
若窗口不可见 (即 isVisible () returns false), the window state will take effect when show () is called. For visible windows, the change is immediate. For example, to toggle between full-screen and normal mode, use the following code:
w->setWindowState(w->windowState() ^ Qt.WindowFullScreen);
In order to restore and activate a minimized window (while preserving its maximized and/or full-screen state), use the following:
w->setWindowState(w->windowState() & ~Qt.WindowMinimized | Qt.WindowActive);
调用此函数将隐藏 Widget。必须调用 show () to make the widget visible 再次。
注意: 在某些窗口系统中 Qt.WindowActive is not immediate, and may be ignored in certain cases.
当窗口状态改变时,Widget 接收 changeEvent () of type QEvent.WindowStateChange .
另请参阅 Qt.WindowState and windowState ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void show() .
Shows the widget and its child widgets. This function is equivalent to setVisible(true).
另请参阅 raise_ (), showEvent (), hide (), setVisible (), showMinimized (), showMaximized (), showNormal (),和 isVisible ().
This event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive widget show events which are passed in the event 参数。
Non-spontaneous show events are sent to widgets immediately before they are shown. The spontaneous show events of windows are delivered afterwards.
Note: A widget receives spontaneous show and hide events when its mapping status is changed by the window system, e.g. a spontaneous hide event when the user minimizes the window, and a spontaneous show event when the window is restored again. After receiving a spontaneous hide event, a widget is still considered visible in the sense of isVisible ().
另请参阅 visible , event (),和 QShowEvent .
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void showFullScreen() .
以全屏模式展示 Widget。
调用此函数仅影响 windows .
要从全屏模式返回,调用 showNormal ().
Full-screen mode works fine under Windows, but has certain problems under X. These problems are due to limitations of the ICCCM protocol that specifies the communication between X11 clients and the window manager. ICCCM simply does not understand the concept of non-decorated full-screen windows. Therefore, the best we can do is to request a borderless window and place and resize it to fill the entire screen. Depending on the window manager, this may or may not work. The borderless window is requested using MOTIF hints, which are at least partially supported by virtually all modern window managers.
An alternative would be to bypass the window manager entirely and create a window with the Qt.X11BypassWindowManagerHint 标志。 This has other severe problems though, like totally broken keyboard focus and very strange effects on desktop changes or when the user raises other windows.
X11 window managers that follow modern post-ICCCM specifications support full-screen mode properly.
另请参阅 showNormal (), showMaximized (), show (), hide (),和 isVisible ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void showMaximized() .
最大化展示 Widget。
调用此函数仅影响 windows .
On X11, this function may not work properly with certain window managers. See the 窗口几何体 文档编制了解解释。
另请参阅 setWindowState (), showNormal (), showMinimized (), show (), hide (),和 isVisible ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void showMinimized() .
以图标形式最小化展示 Widget。
调用此函数仅影响 windows .
另请参阅 showNormal (), showMaximized (), show (), hide (), isVisible (),和 isMinimized ().
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void showNormal() .
Restores the widget after it has been maximized or minimized.
调用此函数仅影响 windows .
另请参阅 setWindowState (), showMinimized (), showMaximized (), show (), hide (),和 isVisible ().
下置 Widget w in the parent widget's stack.
要使这工作,Widget 本身和 w 必须是 siblings.
另请参阅 QWidget.setStyle (), QApplication.setStyle (),和 QApplication.style ().
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive tablet events for the widget.
若重实现此处理程序,非常重要的是 ignore() the event if you do not handle it, so that the widget's parent can interpret it.
默认实现忽略事件。
另请参阅 QTabletEvent.ignore (), QTabletEvent.accept (), event (),和 QTabletEvent .
Returns true if attribute attribute is set on this widget; otherwise returns false.
另请参阅 setAttribute ().
Returns true if the widget is under the mouse cursor; otherwise returns false.
This value is not updated properly during drag and drop operations.
另请参阅 enterEvent () 和 leaveEvent ().
退订 Widget 从给定 gesture type
该函数在 Qt 4.6 引入。
另请参阅 grabGesture () 和 QGestureEvent .
This method is also a Qt slot with the C++ signature void update() .
Updates the widget unless updates are disabled or the widget is hidden.
This function does not cause an immediate repaint; instead it schedules a paint event for processing when Qt returns to the main event loop. This permits Qt to optimize for more speed and less flicker than a call to repaint () does.
多次调用 update() 通常仅仅导致一次 paintEvent () 调用。
Qt 通常先擦除 Widget 区域再 paintEvent () 调用。若 Qt.WA_OpaquePaintEvent widget attribute is set, the widget is responsible for painting all its pixels with an opaque color.
另请参阅 repaint (), paintEvent (), setUpdatesEnabled (),和 指针式时钟范例 .
这是重载函数。
此版本更新矩形 ( x , y , w , h ) 在 Widget 内。
这是重载函数。
此版本更新矩形 rect inside the 小部件。
这是重载函数。
此版本重新描绘区域 rgn 在 Widget 内。
Notifies the layout system that this widget has changed and may need to change geometry.
调用此函数,若 sizeHint () 或 sizePolicy () 已改变。
For explicitly hidden widgets, updateGeometry() is a no-op. The layout system will be notified as soon as the widget is shown.
更新 Widget 的微聚焦。
另请参阅 QInputContext .
返回可以发生描绘事件的未遮盖区域。
For visible widgets, this is an approximation of the area not covered by other widgets; otherwise, this is an empty region.
repaint () function calls this function if necessary, so in general you do not need to call it.
此事件处理程序对于事件 event , can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive wheel events for the widget.
若重实现此处理程序,非常重要的是 ignore() the event if you do not handle it, so that the widget's parent can interpret it.
默认实现忽略事件。
另请参阅 QWheelEvent.ignore (), QWheelEvent.accept (), event (),和 QWheelEvent .
Returns the window for this widget, i.e. the next ancestor widget that has (or could have) a window-system frame.
若 Widget 是窗口,Widget 本身被返回。
典型用法是更改窗口标题:
aWidget->window()->setWindowTitle("New Window Title");
另请参阅 isWindow ().
返回窗口的角色 (或空字符串)。
另请参阅 setWindowRole (), windowIcon ,和 windowTitle .
Returns the current window state. The window state is a OR'ed combination of Qt.WindowState : Qt.WindowMinimized , Qt.WindowMaximized , Qt.WindowFullScreen ,和 Qt.WindowActive .
另请参阅 Qt.WindowState and setWindowState ().
返回此 Widget 的窗口类型。这等同于 windowFlags () & Qt.WindowType_Mask .
另请参阅 windowFlags .
This special event handler can be reimplemented in a subclass to receive native Windows events which are passed in the message 参数。
In your reimplementation of this function, if you want to stop the event being handled by Qt, return true and set result to the value that the window procedure should return. If you return false, this native event is passed back to Qt, which translates the event into a Qt event and sends it to the widget.
警告: This function is not portable.
另请参阅 QApplication.winEventFilter ().
返回 Widget 的窗口系统标识符。
Portable in principle, but if you use it you are probably about to do something non-portable. Be careful.
If a widget is non-native (alien) and winId() is invoked on it, that widget will be provided a native handle.
On Mac OS X, the type returned depends on which framework Qt was linked against. If Qt is using Carbon, the {WId} is actually an HIViewRef. If Qt is using Cocoa, {WId} is a pointer to an NSView.
此值可能在运行时改变。事件带有类型 QEvent.WinIdChange will be sent to the widget following a change in window system identifier.
另请参阅 find ().
This is the default overload of this signal.
此信号被发射当 Widget 的 contextMenuPolicy is Qt.CustomContextMenu , and the user has requested a context menu on the widget. The position pos is the position of the context menu event that the widget receives. Normally this is in widget coordinates. The exception to this rule is QAbstractScrollArea and its subclasses that map the context menu event to coordinates of the viewport() .
另请参阅 mapToGlobal (), QMenu ,和 contextMenuPolicy .